X 2 1 X 2 1
umccalltoaction
Dec 01, 2025 · 8 min read
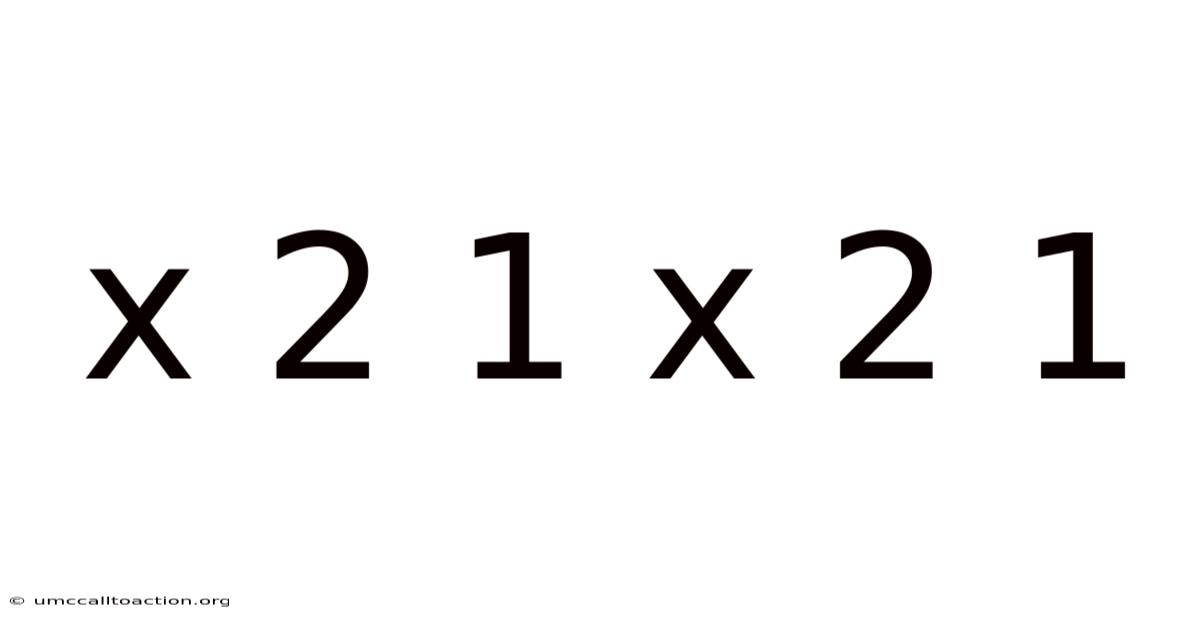
Table of Contents
Understanding and Solving the Equation: x² - 2x + 1 = 0
The equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0 is a fundamental example of a quadratic equation. Mastering how to solve this type of equation is crucial in algebra and calculus. This article will delve into the various methods to solve this equation, providing step-by-step explanations and insights.
Introduction to Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree. The general form is ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and x is the variable. Quadratic equations appear in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics.
In our case, the equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0 fits this form, with a = 1, b = -2, and c = 1. The goal is to find the values of x that satisfy this equation.
Methods to Solve x² - 2x + 1 = 0
There are several methods to solve quadratic equations, including factoring, using the quadratic formula, and completing the square. We will explore each of these methods to solve x² - 2x + 1 = 0.
1. Factoring
Factoring is one of the simplest methods to solve quadratic equations, provided the equation can be easily factored. The idea behind factoring is to express the quadratic equation as a product of two binomials.
Step-by-Step Factoring:
- Identify the factors: Look for two numbers that multiply to give 'c' (in this case, 1) and add up to 'b' (in this case, -2).
- Rewrite the equation: Rewrite the quadratic equation using these factors.
- Factorize: Express the quadratic equation as a product of two binomials.
- Solve for x: Set each factor equal to zero and solve for x.
Applying Factoring to x² - 2x + 1 = 0:
We need two numbers that multiply to 1 and add up to -2. These numbers are -1 and -1. Therefore, we can rewrite the equation as:
x² - x - x + 1 = 0
Now, factor by grouping:
x(x - 1) - 1(x - 1) = 0
Notice that (x - 1) is a common factor:
(x - 1)(x - 1) = 0
This can also be written as:
(x - 1)² = 0
Now, set the factor equal to zero:
x - 1 = 0
Solve for x:
x = 1
Thus, the solution to the equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0 is x = 1.
2. Using the Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a universal method for solving quadratic equations of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. The formula is given by:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / (2a)
Step-by-Step Using the Quadratic Formula:
- Identify a, b, and c: Determine the values of a, b, and c in the quadratic equation.
- Plug into the formula: Substitute the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula.
- Simplify: Simplify the expression to find the values of x.
Applying the Quadratic Formula to x² - 2x + 1 = 0:
In our equation, a = 1, b = -2, and c = 1. Plug these values into the quadratic formula:
x = (-(-2) ± √((-2)² - 4(1)(1))) / (2(1))
Simplify:
x = (2 ± √(4 - 4)) / 2
x = (2 ± √0) / 2
x = (2 ± 0) / 2
x = 2 / 2
x = 1
Again, the solution to the equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0 is x = 1.
3. Completing the Square
Completing the square is another method to solve quadratic equations. This method involves transforming the quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial.
Step-by-Step Completing the Square:
- Ensure a = 1: If a ≠ 1, divide the entire equation by a. In our case, a = 1, so we can skip this step.
- Move the constant term: Move the constant term (c) to the right side of the equation.
- Complete the square: Add (b/2)² to both sides of the equation. This will make the left side a perfect square trinomial.
- Factorize: Factor the perfect square trinomial.
- Solve for x: Take the square root of both sides and solve for x.
Applying Completing the Square to x² - 2x + 1 = 0:
- The equation is already in the form x² - 2x + 1 = 0.
- Move the constant term to the right side: x² - 2x = -1
- Calculate (b/2)²: b = -2, so (b/2)² = (-2/2)² = (-1)² = 1
- Add 1 to both sides of the equation: x² - 2x + 1 = -1 + 1 x² - 2x + 1 = 0
- Factor the left side (which is now a perfect square trinomial): (x - 1)² = 0
- Take the square root of both sides: √(x - 1)² = √0 x - 1 = 0
- Solve for x: x = 1
Thus, the solution to the equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0 is x = 1.
Understanding the Discriminant
The discriminant is a part of the quadratic formula that gives us information about the nature of the roots (solutions) of the quadratic equation. The discriminant is the expression inside the square root: b² - 4ac.
- If b² - 4ac > 0, the equation has two distinct real roots.
- If b² - 4ac = 0, the equation has one real root (a repeated root).
- If b² - 4ac < 0, the equation has two complex roots.
In our case, for the equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0:
Discriminant = b² - 4ac = (-2)² - 4(1)(1) = 4 - 4 = 0
Since the discriminant is 0, the equation has one real root, which we found to be x = 1.
Graphical Interpretation
The equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0 represents a parabola in the Cartesian coordinate system. The solutions to the equation are the x-intercepts of the parabola. In other words, they are the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis.
For the equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0, the graph of y = x² - 2x + 1 is a parabola that touches the x-axis at only one point, x = 1. This confirms that the equation has a single real root.
Real-World Applications
Quadratic equations like x² - 2x + 1 = 0 are not just abstract mathematical concepts. They have practical applications in various fields. Here are a few examples:
-
Physics:
- Projectile Motion: Quadratic equations are used to describe the trajectory of projectiles, such as balls thrown in the air. The equation can help determine the maximum height reached and the distance traveled.
- Simple Harmonic Motion: In the analysis of simple harmonic motion, quadratic equations can arise when calculating energy and displacement.
-
Engineering:
- Structural Design: Engineers use quadratic equations to calculate stresses and strains in structures, ensuring they can withstand loads and forces.
- Circuit Analysis: In electrical engineering, quadratic equations are used in the analysis of circuits, particularly in determining impedance and power.
-
Economics:
- Supply and Demand: Quadratic equations can model supply and demand curves, helping economists understand market equilibrium.
- Optimization Problems: Businesses use quadratic equations to optimize profits, costs, and production levels.
-
Computer Science:
- Algorithm Design: Quadratic equations can appear in the analysis of algorithms, particularly in determining time complexity and efficiency.
- Computer Graphics: Quadratic equations are used to create curves and surfaces in computer graphics, enabling realistic rendering of objects.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When solving quadratic equations, it's important to avoid common mistakes that can lead to incorrect solutions. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
-
Incorrect Factoring:
- Mistake: Incorrectly identifying the factors that multiply to 'c' and add up to 'b'.
- Prevention: Double-check the factors to ensure they satisfy both conditions.
-
Misapplication of the Quadratic Formula:
- Mistake: Plugging the values of a, b, and c incorrectly into the formula.
- Prevention: Carefully write down the values of a, b, and c and double-check the substitution.
-
Errors in Completing the Square:
- Mistake: Forgetting to add (b/2)² to both sides of the equation or incorrectly calculating (b/2)².
- Prevention: Follow each step meticulously and double-check the calculations.
-
Algebraic Errors:
- Mistake: Making errors in simplifying expressions, such as incorrectly distributing signs or combining like terms.
- Prevention: Practice algebraic manipulations and double-check each step.
-
Ignoring the Discriminant:
- Mistake: Not considering the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots, which can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Prevention: Calculate the discriminant before solving the equation to understand the type of solutions to expect.
Advanced Techniques and Extensions
Beyond the basic methods, there are advanced techniques and extensions related to quadratic equations that are useful in more complex problems.
-
Vieta's Formulas:
- Vieta's formulas relate the coefficients of a polynomial to sums and products of its roots. For a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0 with roots x₁ and x₂, Vieta's formulas are:
- x₁ + x₂ = -b/a
- x₁ * x₂ = c/a
- These formulas can be used to quickly find the sum and product of the roots without actually solving the equation.
- Vieta's formulas relate the coefficients of a polynomial to sums and products of its roots. For a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0 with roots x₁ and x₂, Vieta's formulas are:
-
Transformations of Quadratic Equations:
- Sometimes, it is useful to transform a quadratic equation into a different form to simplify the solution process. For example, substituting variables or using trigonometric identities.
-
Quadratic Inequalities:
- Quadratic inequalities involve comparing a quadratic expression to a constant or another expression. Solving quadratic inequalities involves finding the intervals where the quadratic expression satisfies the inequality.
-
Systems of Quadratic Equations:
- Systems of quadratic equations involve solving multiple quadratic equations simultaneously. These systems can be solved using substitution, elimination, or graphical methods.
Conclusion
The equation x² - 2x + 1 = 0 serves as an excellent example to illustrate various methods for solving quadratic equations. Whether through factoring, using the quadratic formula, or completing the square, the solution remains consistent: x = 1. Understanding these methods not only helps in solving equations but also provides a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. The discriminant provides valuable insights into the nature of the roots, and graphical interpretations offer a visual understanding of the solutions. By avoiding common mistakes and practicing regularly, one can master the art of solving quadratic equations and apply this knowledge to real-world problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Surgical Pathology Levels Are Determined By
Dec 02, 2025
-
Images Of The Month Of September
Dec 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Leukocyte
Dec 02, 2025
-
How Many People Qualify For Aime
Dec 02, 2025
-
How To Find Overlap Between Two Lists In Excel
Dec 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 1 X 2 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.