What Is The Difference Between 6 And 6x
umccalltoaction
Dec 05, 2025 · 10 min read
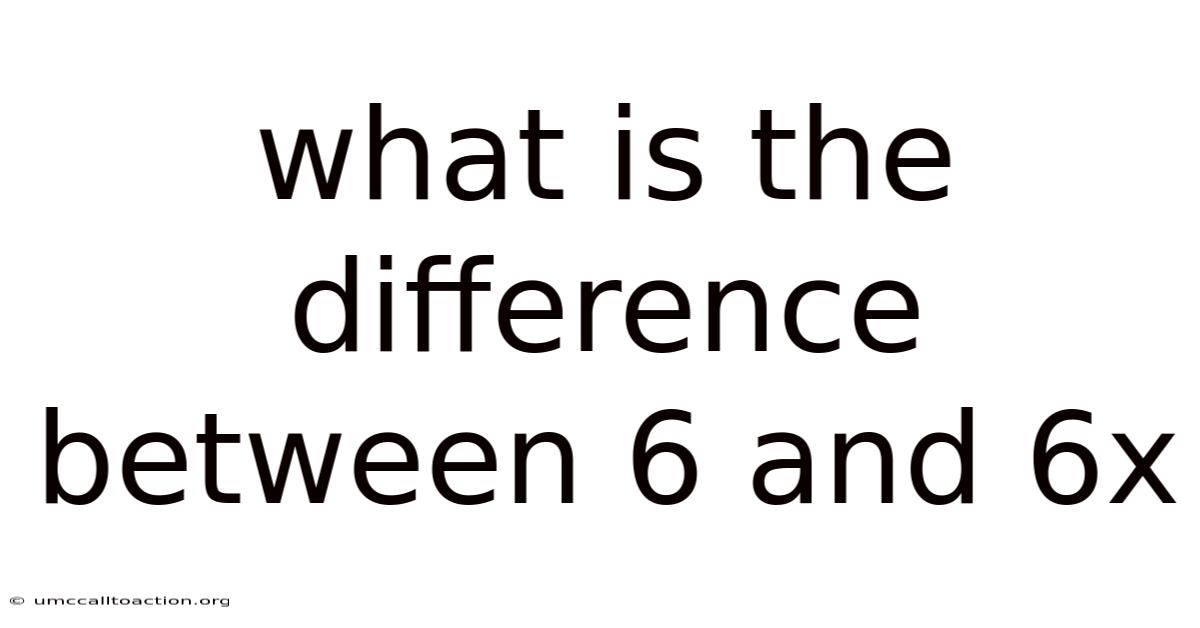
Table of Contents
Here's a detailed exploration of the distinction between "6" and "6x", delving into their mathematical meanings, applications, and potential for misinterpretation.
Unveiling the Difference: 6 vs. 6x
At first glance, "6" and "6x" might appear similar, especially to someone unfamiliar with basic algebra. However, they represent fundamentally different mathematical concepts. "6" is a constant, a fixed numerical value. It signifies a specific quantity, representing six units. On the other hand, "6x" is an algebraic expression representing a variable term. It indicates six times the value of 'x,' where 'x' is a variable that can hold different numerical values. Understanding this core difference is crucial for grasping more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving. This exploration will dissect these differences, explore their applications, and shed light on potential areas of confusion.
The Constant: Understanding "6"
The number 6 is a cornerstone of mathematics, representing a specific quantity. It's a natural number, an integer, and a real number, all rolled into one. Its properties and applications are vast and fundamental.
Properties of the Number 6
- Natural Number: 6 belongs to the set of natural numbers (1, 2, 3, ...), representing a positive whole number.
- Integer: It's also an integer, a whole number that can be positive, negative, or zero.
- Real Number: 6 is a real number, meaning it can be found on the number line.
- Even Number: 6 is divisible by 2, making it an even number.
- Composite Number: It's a composite number because it has factors other than 1 and itself (2 and 3).
- Perfect Number: 6 is the smallest perfect number. A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding the number itself). The proper divisors of 6 are 1, 2, and 3, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.
Applications of "6" in Mathematics and Everyday Life
The number 6 is ubiquitous, appearing in various mathematical contexts and everyday scenarios:
- Counting: The most basic application is counting objects. We use "6" to represent a collection of six items.
- Arithmetic: 6 is used in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. For example, 3 + 3 = 6, 12 - 6 = 6, 2 x 3 = 6, and 36 / 6 = 6.
- Geometry: A hexagon is a polygon with six sides and six angles.
- Time: There are 60 seconds in a minute and often references to six o'clock.
- Measurement: Units of measurement sometimes involve 6, such as in certain construction or culinary contexts.
- Combinations and Permutations: 6 appears in calculating combinations and permutations, such as the number of ways to arrange six distinct objects.
- Probability: When calculating probabilities, 6 can represent the number of favorable outcomes or the total number of possible outcomes. For instance, the probability of rolling a specific number on a standard six-sided die is 1/6.
Why "6" is Always "6"
The crucial characteristic of "6" is its fixed value. It doesn't change based on any external factors or variables. It always represents six units, regardless of the context. This constancy makes it a fundamental building block in mathematical calculations and a reliable representation of quantity.
The Variable Term: Understanding "6x"
"6x" is an algebraic expression, not a fixed number. It represents a product: 6 multiplied by the variable 'x.' The value of "6x" depends entirely on the value assigned to the variable 'x.'
Components of "6x"
- Coefficient: The number 6 in "6x" is called the coefficient. It's the numerical factor that multiplies the variable.
- Variable: 'x' is the variable. A variable is a symbol (usually a letter) that represents an unknown or changeable value.
How the Value of "6x" Changes with "x"
The essence of "6x" lies in its variability. Let's explore how the value of "6x" changes as we assign different values to 'x':
- If x = 1, then 6x = 6 * 1 = 6
- If x = 2, then 6x = 6 * 2 = 12
- If x = 3, then 6x = 6 * 3 = 18
- If x = 0, then 6x = 6 * 0 = 0
- If x = -1, then 6x = 6 * (-1) = -6
- If x = 0.5, then 6x = 6 * 0.5 = 3
- If x = π (pi ≈ 3.14159), then 6x = 6 * π ≈ 18.84954
As you can see, the value of "6x" is directly proportional to the value of 'x.' This relationship is fundamental to understanding algebraic expressions and equations.
Applications of "6x" in Algebra and Beyond
"6x" and similar algebraic expressions are the building blocks of algebra and have widespread applications:
- Algebraic Equations: "6x" appears in equations that need to be solved for 'x.' For example, in the equation 6x + 3 = 15, we need to isolate 'x' to find its value.
- Functions: In function notation, we might have f(x) = 6x. This defines a function where the output is six times the input.
- Graphing: The expression "y = 6x" represents a straight line on a graph. The coefficient 6 determines the slope of the line.
- Modeling Real-World Scenarios: "6x" can model relationships between quantities. For example, if 'x' represents the number of hours worked and 6 represents the hourly wage, then "6x" represents the total earnings.
- Calculus: In calculus, expressions like "6x" are used to find derivatives and integrals, which are essential for understanding rates of change and accumulation.
- Physics: "6x" can represent physical quantities. For instance, if 'x' is time, and 6 is acceleration, "6x" could represent velocity.
Why "6x" is Not Always "6"
The critical takeaway is that "6x" only equals "6" when x = 1. Otherwise, "6x" represents a different value, dependent on the value of 'x.' This dependence on a variable is what distinguishes it from the constant "6."
Side-by-Side Comparison: 6 vs. 6x
To solidify the understanding, here's a table summarizing the key differences between "6" and "6x":
| Feature | 6 | 6x |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Constant | Algebraic Expression |
| Value | Fixed, always six | Variable, depends on the value of 'x' |
| Represents | A specific quantity | Six times the value of 'x' |
| Contains | A number | A coefficient and a variable |
| Changes with 'x' | No | Yes |
| Usage | Direct counting, basic arithmetic | Algebra, functions, modeling, calculus |
| Example | Six apples, six seconds | 6x + 2 = 14, f(x) = 6x |
Common Misconceptions and How to Avoid Them
Confusion between "6" and "6x" often arises from a lack of understanding of basic algebra or careless reading. Here are some common misconceptions and how to address them:
- Misconception: Assuming "6x" always equals "6."
- Correction: Emphasize that "6x" is equal to "6" only when x = 1. Otherwise, its value changes depending on the value of 'x.'
- Misconception: Treating "6x" as a single unit like "6," ignoring the multiplication.
- Correction: Break down "6x" into its components: 6 * x. Clearly explain that it represents six multiplied by the value of 'x.'
- Misconception: Confusing "6x" with "6 + x" or "x^6".
- Correction: Carefully explain the different mathematical operations:
- "6x" means 6 * x (multiplication).
- "6 + x" means 6 plus x (addition).
- "x^6" means x raised to the power of 6 (exponentiation).
- Correction: Carefully explain the different mathematical operations:
- Misconception: Difficulty understanding the concept of a variable.
- Correction: Provide real-world examples of variables. For instance, the temperature outside is a variable because it changes throughout the day. The number of students in a class can also be a variable if students enroll or drop out.
Tips for Avoiding Confusion:
- Pay Attention to Detail: Carefully read mathematical expressions and identify the operations and variables involved.
- Practice Regularly: Solve various algebraic problems involving variables and coefficients.
- Visualize the Concepts: Use diagrams or graphs to represent the relationship between "6x" and 'x.'
- Ask Questions: Don't hesitate to ask for clarification if you're unsure about something.
- Use Concrete Examples: Relate the concepts to real-world scenarios to make them more understandable.
- Be Mindful of Context: Always consider the context in which the expression appears. Is it part of an equation? Is it defining a function? Understanding the context can provide valuable clues.
Real-World Examples Illustrating the Difference
Let's explore some real-world examples to further illustrate the difference between "6" and "6x":
- Example 1: Cookies
- If you have 6 cookies, you have a fixed quantity of cookies. This is represented by the number 6.
- If you have 'x' boxes of cookies, and each box contains 6 cookies, then you have "6x" cookies in total. The total number of cookies depends on the number of boxes you have. If you have 3 boxes (x=3), you have 6 * 3 = 18 cookies.
- Example 2: Distance
- If you travel 6 kilometers, you have covered a fixed distance. This is represented by the number 6.
- If you travel at a speed of 6 kilometers per hour for 'x' hours, then the total distance you travel is "6x" kilometers. The total distance depends on the duration of your travel. If you travel for 2 hours (x=2), you cover a distance of 6 * 2 = 12 kilometers.
- Example 3: Cost
- If an item costs $6, its price is fixed. This is represented by the number 6.
- If you buy 'x' items, and each item costs $6, then the total cost is "6x" dollars. The total cost depends on the number of items you buy. If you buy 5 items (x=5), the total cost is 6 * 5 = $30.
- Example 4: Ingredients
- A recipe calls for 6 eggs. This is a fixed quantity.
- You are baking 'x' batches of the recipe. Each batch requires 6 eggs, so you need "6x" eggs. If you are making 4 batches (x=4), you need 6 * 4 = 24 eggs.
These examples highlight how "6" represents a fixed quantity, while "6x" represents a quantity that varies depending on the value of 'x.'
Advanced Applications: Beyond the Basics
While the core difference is fundamental, understanding "6" and "6x" is crucial for tackling more advanced mathematical concepts:
- Polynomials: Expressions like 6x^2 + 3x - 2 involve both constants (like -2) and variable terms (like 6x^2 and 3x). Understanding the role of coefficients and variables is essential for manipulating and solving polynomial equations.
- Calculus: Derivatives and integrals involve finding rates of change and areas under curves. These calculations heavily rely on understanding how variable terms like "6x" behave. The derivative of 6x with respect to x is simply 6, highlighting the connection between the variable term and its constant rate of change.
- Linear Algebra: In linear algebra, systems of linear equations are often represented using matrices and vectors. These systems involve multiple variables and coefficients, and solving them requires a solid understanding of how these components interact.
- Differential Equations: Differential equations describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives. Solving these equations often involves manipulating variable terms and constants to find the unknown function.
The Importance of a Solid Foundation
The distinction between "6" and "6x" might seem simple, but it's a crucial building block for mathematical literacy. A solid understanding of this difference is essential for:
- Success in Algebra: Mastering the concepts of variables, coefficients, and algebraic expressions is fundamental to success in algebra.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to translate real-world problems into mathematical equations and solve them depends on understanding the role of constants and variables.
- Critical Thinking: Understanding the relationship between quantities and variables fosters critical thinking skills that are valuable in various aspects of life.
- STEM Fields: A strong mathematical foundation is essential for pursuing careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
The difference between "6" and "6x" lies in their nature: "6" is a constant, representing a fixed value, while "6x" is an algebraic expression, representing a variable term whose value depends on 'x.' Understanding this distinction is crucial for grasping fundamental mathematical concepts and tackling more advanced problems. By paying attention to detail, practicing regularly, and relating concepts to real-world scenarios, you can avoid common misconceptions and build a solid foundation for mathematical success. The journey to mastering mathematics begins with understanding the basics, and differentiating between constants and variables is a vital step in that journey. Remember, "6" is always "6," but "6x" can be anything, depending on the value of 'x.'
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between 6 And 6x . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.