What Is 3 4 Divided By 2 5
umccalltoaction
Dec 04, 2025 · 8 min read
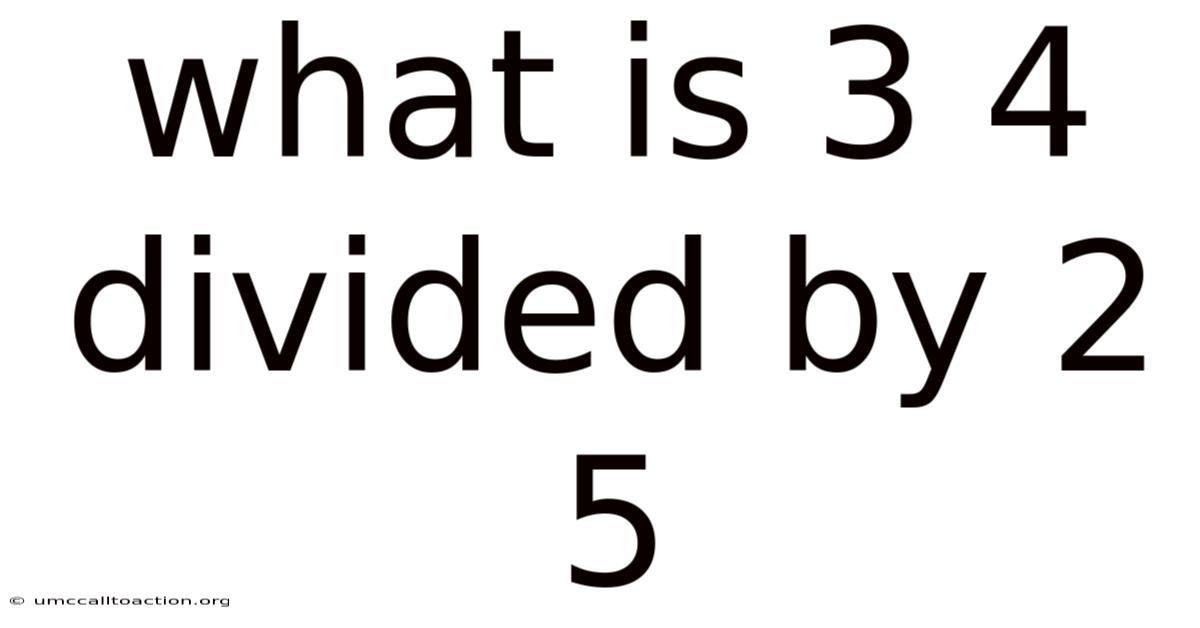
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery: What is 3/4 Divided by 2/5?
The world of fractions can sometimes feel like a labyrinth of numerators and denominators. Among the fundamental operations we perform with fractions, division often poses a unique challenge. Let's dive deep into understanding what it truly means to divide 3/4 by 2/5, exploring the concept behind it, the step-by-step process of solving it, and some real-world applications.
The Foundation: Understanding Fractions
Before we tackle the division itself, let's ensure we have a solid grasp of what fractions represent. A fraction is simply a way to represent a part of a whole. It's composed of two key components:
- Numerator: The number above the line in a fraction. It represents how many parts we have.
- Denominator: The number below the line in a fraction. It represents the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
So, the fraction 3/4 signifies that we have 3 parts out of a total of 4 equal parts. Similarly, 2/5 means we possess 2 parts out of 5 equal divisions.
Conceptualizing Division with Fractions
Dividing fractions isn't as straightforward as dividing whole numbers. When we divide one number by another, we're essentially asking: "How many times does the second number fit into the first?" Applying this to fractions can be a bit tricky.
For example, asking "What is 3/4 divided by 2/5?" is like asking: "How many portions of size 2/5 are there in a portion of size 3/4?" To answer this, we need to understand the concept of reciprocals.
The Power of Reciprocals
The reciprocal of a fraction is simply that fraction flipped upside down. To find the reciprocal, you swap the numerator and the denominator.
- The reciprocal of 2/5 is 5/2.
- The reciprocal of 7/8 is 8/7.
- The reciprocal of 1/3 is 3/1 (which is the same as 3).
Why are reciprocals so important in fraction division? Because dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal. This transformation makes the process much easier to handle.
The Algorithm: Dividing 3/4 by 2/5 - Step-by-Step
Now, let's apply this knowledge to solve our original problem: 3/4 divided by 2/5. Here's the step-by-step process:
- Identify the fractions: We have 3/4 as the dividend (the number being divided) and 2/5 as the divisor (the number we are dividing by).
- Find the reciprocal of the divisor: The reciprocal of 2/5 is 5/2.
- Change the division to multiplication: Rewrite the problem as a multiplication problem, using the reciprocal: 3/4 ÷ 2/5 becomes 3/4 × 5/2.
- Multiply the numerators: Multiply the numerators of the two fractions: 3 × 5 = 15.
- Multiply the denominators: Multiply the denominators of the two fractions: 4 × 2 = 8.
- Write the result as a fraction: The result is 15/8.
- Simplify the fraction (if possible): In this case, 15/8 is an improper fraction (the numerator is larger than the denominator). We can convert it to a mixed number. 8 goes into 15 once, with a remainder of 7. Therefore, 15/8 is equal to 1 7/8.
So, 3/4 divided by 2/5 equals 15/8 or 1 7/8.
Why Does This Work? The Underlying Logic
It's crucial not just to memorize the steps, but to understand why dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal. Here's a conceptual explanation:
Think about dividing by 1/2. Dividing something by 1/2 is the same as doubling it. For example, 10 divided by 1/2 is 20. This is because you're asking "How many halves are in 10?" There are twenty halves in ten whole units. Multiplying by 2 (the reciprocal of 1/2) achieves the same result: 10 * 2 = 20.
The same principle applies to other fractions. Dividing by 2/5 is essentially asking how many "two-fifths" are contained within a given quantity. Multiplying by the reciprocal, 5/2, accomplishes the same calculation in a more direct and efficient manner. It's a mathematical shortcut based on the properties of inverse operations.
Real-World Applications of Fraction Division
Fractions and their division pop up in various real-world scenarios:
- Cooking: Imagine you have 3/4 of a cup of flour and a recipe calls for 2/5 of a cup of flour per batch of cookies. Dividing 3/4 by 2/5 tells you how many batches of cookies you can make.
- Construction: Let's say a contractor needs to cut pieces of wood that are 2/5 of a meter long from a plank that is 3/4 of a meter long. Dividing 3/4 by 2/5 will determine how many pieces the contractor can cut.
- Travel: If you've covered 3/4 of a journey and each segment of the journey is 2/5 of the total distance, dividing 3/4 by 2/5 shows you how many segments you've completed.
- Sharing: You have 3/4 of a pizza left and want to share it equally among 2/5 of your friend group (perhaps only some friends are hungry). Dividing 3/4 by 2/5 represents the portion of a whole pizza each of those friends will receive.
- Scaling Recipes: A recipe calls for certain ingredient amounts to serve a particular number of people. If you need to scale the recipe up or down, you'll often need to divide fractions. For example, if the original recipe yields 2/5 of a cake and you only want 3/4 of that amount, you would perform the division to adjust ingredient quantities.
These are just a few examples; fraction division is a valuable tool in numerous fields requiring precise measurement and proportional reasoning.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While the process itself is relatively straightforward, certain common errors can occur when dividing fractions. Being aware of these potential pitfalls can help prevent mistakes:
- Forgetting to take the reciprocal: This is the most frequent mistake. Remember, you must flip the second fraction (the divisor) before multiplying.
- Multiplying straight across without taking the reciprocal: This will lead to an incorrect answer. The reciprocal is crucial for changing the operation from division to multiplication.
- Simplifying before multiplying: While simplifying can make the numbers smaller, it's generally best to multiply first and then simplify the resulting fraction. Simplifying beforehand can sometimes be confusing.
- Confusion between dividend and divisor: Ensure you know which fraction is being divided and which fraction you are dividing by. The order matters! The dividend comes first, followed by the division symbol, and then the divisor.
- Difficulty converting improper fractions to mixed numbers: Always present your final answer in the simplest form, which often involves converting improper fractions into mixed numbers.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
While dividing simple fractions is essential, understanding the concept opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts:
- Dividing Mixed Numbers: To divide mixed numbers, first convert them into improper fractions. Then, proceed with the standard division process (multiply by the reciprocal). For example, if you want to divide 2 1/2 by 1 1/4, you would convert them to 5/2 and 5/4, respectively. Then, you would divide 5/2 by 5/4, which is the same as multiplying 5/2 by 4/5.
- Dividing Complex Fractions: Complex fractions are fractions where either the numerator, the denominator, or both contain fractions themselves. To simplify a complex fraction, you essentially treat it as a division problem. For example, the complex fraction (1/2) / (3/4) is the same as 1/2 divided by 3/4.
- Algebraic Fractions: The same principles of fraction division apply to algebraic fractions, where the numerator and denominator are algebraic expressions.
- Ratio and Proportion: Division of fractions is fundamental to understanding ratios and proportions, which are crucial in various mathematical and scientific applications. Understanding how to manipulate fractions helps in solving problems related to scaling, similarity, and comparative analysis.
The Importance of Practice
As with any mathematical skill, mastery of fraction division requires consistent practice. Work through various examples, starting with simple problems and gradually progressing to more complex ones. Utilize online resources, textbooks, and worksheets to reinforce your understanding. The more you practice, the more comfortable and confident you will become with this fundamental operation.
Beyond Rote Memorization: Fostering Conceptual Understanding
While memorizing the steps for dividing fractions is helpful, it's equally important to cultivate a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts. Encourage exploration with visual aids, such as fraction bars or pie charts, to represent fractions and their division. Ask questions like:
- "What does it mean to divide 3/4 by 2/5?"
- "Why does multiplying by the reciprocal work?"
- "Can you think of a real-world scenario where you might need to divide fractions?"
By promoting conceptual understanding, you empower learners to apply their knowledge in diverse contexts and solve problems with greater confidence.
In Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Division
Dividing fractions might initially seem daunting, but with a solid grasp of the concepts and a methodical approach, it becomes a manageable and valuable skill. Remember the key steps: find the reciprocal of the divisor, change the division to multiplication, multiply the numerators and denominators, and simplify the result. Most importantly, strive to understand why this process works. With consistent practice and a focus on conceptual understanding, you can unlock the power of fraction division and apply it to a wide range of real-world scenarios. The answer to "What is 3/4 divided by 2/5?" is 15/8 or 1 7/8 – but the real value lies in understanding the journey to get there.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Do You Do If There Are Two Medians
Dec 04, 2025
-
4 Major Areas Of Water Storage On Earth
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Number Is 40 Greater Than 115
Dec 04, 2025
-
Sample Of Acknowledgement For Research Paper
Dec 04, 2025
-
Fico Score Decreased For No Reason
Dec 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 3 4 Divided By 2 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.