G Cm 3 To G Mm 3
umccalltoaction
Dec 04, 2025 · 8 min read
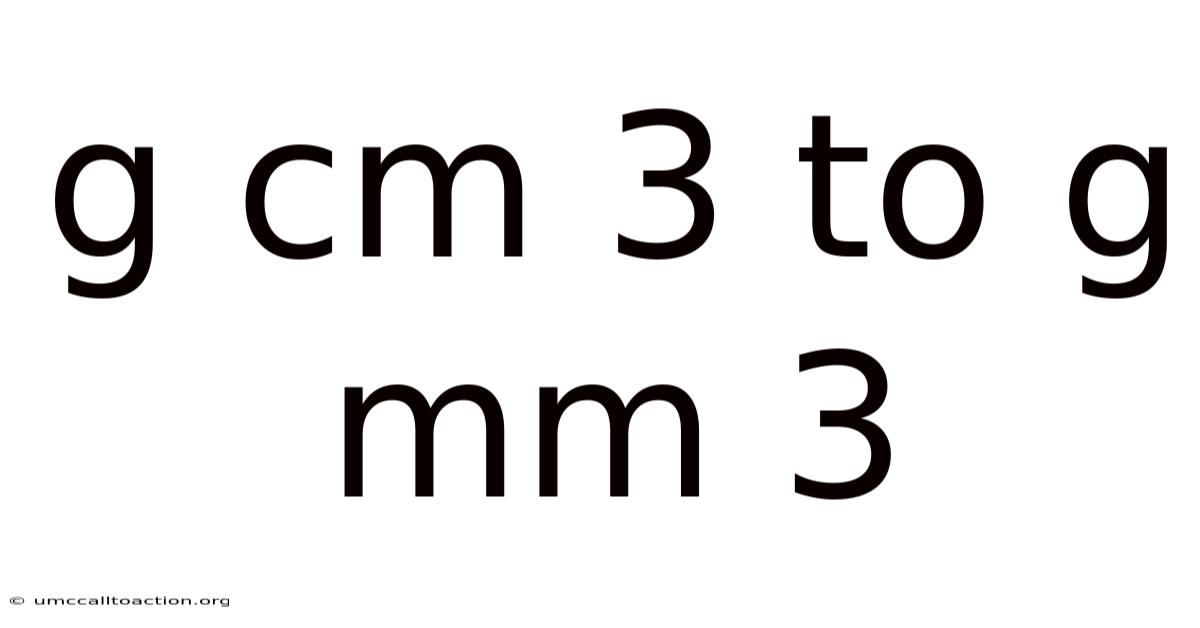
Table of Contents
Converting between units can sometimes feel like navigating a maze, but it's a crucial skill in various fields, especially in science and engineering, and understanding how to convert from g/cm³ to g/mm³ is no exception. This seemingly simple conversion holds significance when dealing with densities in different scales, ensuring accuracy and consistency in calculations.
Understanding Density
Density is a fundamental property of matter that describes how much mass is contained in a given volume. It's typically expressed as mass per unit volume, and its formula is:
Density = Mass / Volume
The standard unit of density in the International System of Units (SI) is kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). However, grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) and grams per cubic millimeter (g/mm³) are also commonly used, especially when dealing with smaller scales.
Why Convert Between g/cm³ and g/mm³?
The conversion between g/cm³ and g/mm³ is essential for several reasons:
-
Scale of Measurement: Different applications require different scales. For instance, material densities in macroscopic engineering projects might be conveniently expressed in g/cm³, while microscopic or nanoscale applications might benefit from using g/mm³.
-
Compatibility: Converting between units ensures that all values are expressed in a consistent unit, allowing for accurate comparisons and calculations.
-
Clarity: Using appropriate units can simplify complex calculations and make results easier to interpret.
The Conversion Factor
The key to converting between g/cm³ and g/mm³ lies in understanding the relationship between cubic centimeters and cubic millimeters.
- 1 cm = 10 mm
Therefore:
- 1 cm³ = (10 mm)³ = 1000 mm³
This means that one cubic centimeter is equal to one thousand cubic millimeters. To convert from g/cm³ to g/mm³, you need to adjust the volume component of the density.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
To convert a density value from g/cm³ to g/mm³, follow these simple steps:
-
Understand the Given Value: Identify the density value you wish to convert. For example, let's say we want to convert the density of aluminum, which is approximately 2.7 g/cm³, to g/mm³.
-
Apply the Conversion Factor: Since 1 cm³ = 1000 mm³, you need to divide the density value in g/cm³ by 1000 to get the equivalent value in g/mm³.
- Density in g/mm³ = Density in g/cm³ / 1000
-
Perform the Calculation:
- Density of aluminum in g/mm³ = 2.7 g/cm³ / 1000 = 0.0027 g/mm³
-
State the Result: The density of aluminum is 0.0027 g/mm³.
Example Conversions
Let's go through a few more examples to solidify your understanding of the conversion process:
Example 1: Converting the Density of Water
The density of water is approximately 1 g/cm³. Let's convert this to g/mm³.
- Density in g/mm³ = 1 g/cm³ / 1000 = 0.001 g/mm³
Therefore, the density of water is 0.001 g/mm³.
Example 2: Converting the Density of Iron
The density of iron is approximately 7.87 g/cm³. Let's convert this to g/mm³.
- Density in g/mm³ = 7.87 g/cm³ / 1000 = 0.00787 g/mm³
Therefore, the density of iron is 0.00787 g/mm³.
Example 3: Converting the Density of Gold
The density of gold is approximately 19.3 g/cm³. Let's convert this to g/mm³.
- Density in g/mm³ = 19.3 g/cm³ / 1000 = 0.0193 g/mm³
Therefore, the density of gold is 0.0193 g/mm³.
Practical Applications
Understanding and applying this conversion has numerous practical applications across various fields:
-
Materials Science: In materials science, knowing the density of materials in different units is crucial for designing and analyzing structures, components, and devices. For example, when working with thin films or microstructures, expressing density in g/mm³ might be more convenient.
-
Engineering: Engineers often work with materials at different scales. Civil engineers might use g/cm³ for bulk materials like concrete, while mechanical engineers might use g/mm³ for precision components in machines.
-
Chemistry: Chemists often deal with small quantities of substances, and expressing densities in g/mm³ can be useful for calculating concentrations and volumes in microfluidic devices and other small-scale systems.
-
Geology: Geologists use density measurements to study the composition of rocks and minerals. The ability to convert between different units allows for seamless integration of data from various sources.
-
Environmental Science: Environmental scientists use density measurements to study soil composition, water quality, and air pollution. Converting between g/cm³ and g/mm³ can be useful for analyzing samples at different scales.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While the conversion between g/cm³ and g/mm³ is relatively straightforward, it's essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results:
-
Incorrect Conversion Factor: The most common mistake is using the wrong conversion factor. Remember that 1 cm³ = 1000 mm³, so you should divide by 1000 when converting from g/cm³ to g/mm³.
-
Unit Confusion: Ensure that you are consistent with your units throughout the calculation. Mixing up centimeters and millimeters can lead to significant errors.
-
Calculation Errors: Double-check your calculations to avoid simple arithmetic mistakes. Using a calculator can help reduce the likelihood of errors.
-
Forgetting to Convert: Sometimes, the need for conversion is overlooked. Always ensure that all values are in consistent units before performing calculations.
Alternative Methods for Conversion
While the direct conversion method is the most straightforward, there are alternative approaches you can use:
-
Dimensional Analysis: Dimensional analysis involves tracking the units throughout the calculation to ensure they cancel out correctly. This method can be particularly useful for complex conversions involving multiple units.
-
Online Converters: Numerous online unit converters can perform the conversion automatically. These tools can be convenient for quick conversions, but it's still essential to understand the underlying principles to verify the results.
Advanced Considerations
For more advanced applications, there are several additional factors to consider:
-
Temperature and Pressure: Density is temperature and pressure-dependent. When working with high-precision measurements, it's essential to account for these factors and use appropriate correction factors.
-
Material Composition: The density of a material can vary depending on its composition. For example, the density of steel can vary depending on the alloy composition.
-
Isotopic Composition: For some elements, the isotopic composition can affect the density. This is particularly important for high-precision measurements in nuclear and isotope science.
The Importance of Precision
In scientific and engineering applications, precision is paramount. Accurate density measurements and conversions are crucial for ensuring the reliability and validity of results. Using the correct units, avoiding common mistakes, and considering advanced factors can all contribute to improved precision.
Historical Context
The development of standardized units and conversion methods has been a gradual process, evolving alongside scientific and technological advancements. The metric system, which includes units like grams, centimeters, and millimeters, was developed in France in the late 18th century and has since been adopted by most countries around the world.
The standardization of units has greatly facilitated communication and collaboration among scientists and engineers from different countries and disciplines. It has also played a key role in the advancement of technology and innovation.
Real-World Examples
To further illustrate the importance of converting between g/cm³ and g/mm³, let's consider some real-world examples:
-
Microfabrication: In microfabrication, devices are created with dimensions on the micrometer scale. When calculating the mass of thin films or microstructures, it's often more convenient to use g/mm³ as the unit of density.
-
Nanotechnology: In nanotechnology, materials are manipulated at the atomic and molecular level. Understanding densities in g/mm³ is essential for calculating the mass and volume of nanomaterials.
-
Aerospace Engineering: Aerospace engineers use a variety of materials with different densities. Converting between g/cm³ and g/mm³ allows for accurate calculations of weight and balance in aircraft and spacecraft design.
-
Medical Devices: Medical devices often require precise measurements and calculations. Converting between g/cm³ and g/mm³ can be important for designing devices such as implants and drug delivery systems.
Impact on Technological Advancement
The ability to accurately convert between different units has had a profound impact on technological advancement. It has enabled scientists and engineers to design and build increasingly complex and sophisticated devices and systems. From smartphones to satellites, modern technology relies on precise measurements and calculations that would not be possible without standardized units and conversion methods.
Educational Implications
Teaching students how to convert between different units is an essential part of science and engineering education. It helps them develop critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities. Understanding the relationship between different units also fosters a deeper appreciation for the importance of measurement and precision in scientific and engineering work.
Future Trends
As technology continues to advance, the need for accurate unit conversions will only become more important. New materials and devices are being developed at increasingly smaller scales, requiring even more precise measurements and calculations. The development of new and improved unit conversion methods will be essential for supporting these advances.
Additionally, the increasing use of computer simulations and modeling in science and engineering will require sophisticated tools for handling unit conversions. These tools will need to be able to automatically convert between different units and ensure consistency throughout the simulation.
Conclusion
The conversion from g/cm³ to g/mm³ is a fundamental skill in many scientific and engineering disciplines. It allows for accurate density measurements and calculations at different scales, ensuring consistency and compatibility. By understanding the conversion factor, following the step-by-step process, and avoiding common mistakes, you can confidently convert between these units and apply them to a wide range of practical applications.
In summary, mastering this conversion is not just about performing a mathematical operation; it's about developing a deeper understanding of the relationship between mass, volume, and density, and appreciating the importance of precision in scientific and engineering endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 Month Old Not Making Eye Contact
Dec 04, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between Inter And Intra
Dec 04, 2025
-
Excel Count Specific Characters In Cell
Dec 04, 2025
-
Soil Conservation Service Site 17 Reservoir
Dec 04, 2025
-
Is A 1998 Quarter Worth Anything
Dec 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about G Cm 3 To G Mm 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.