1 1 16 Divided By 2
umccalltoaction
Dec 03, 2025 · 7 min read
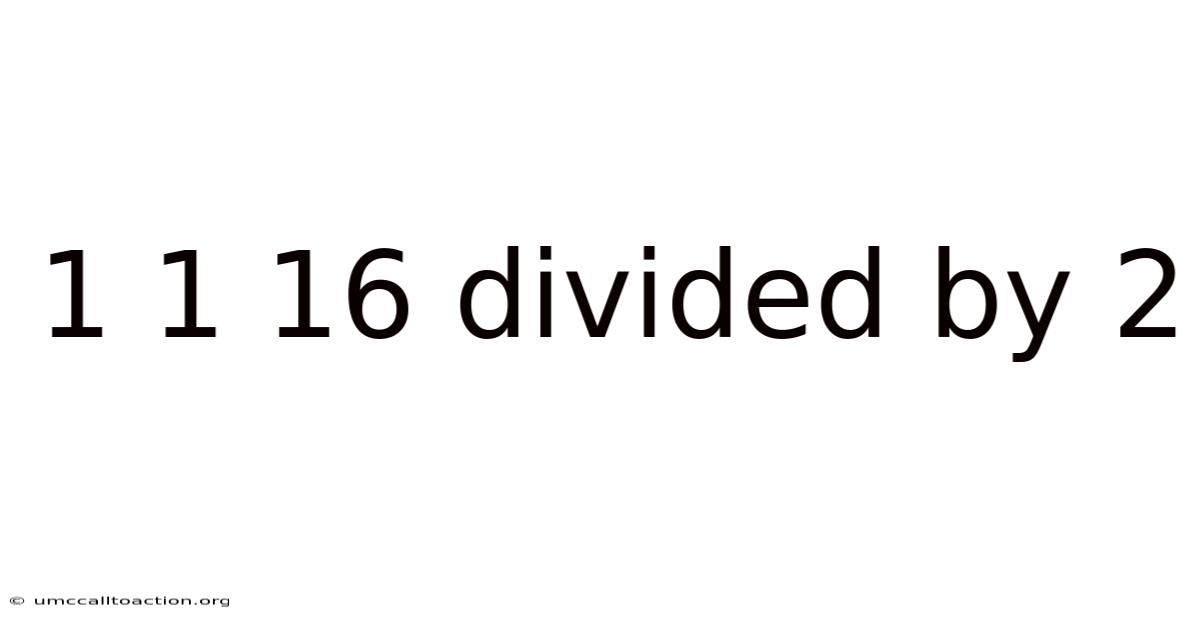
Table of Contents
The seemingly simple arithmetic problem of "1 1 16 divided by 2" often leads to confusion because of the way it's written and interpreted. To unravel this, we need to break down the different possible interpretations, clarify the mathematical order of operations, and then solve the problem accurately.
Understanding the Ambiguity
The expression "1 1 16 divided by 2" is ambiguous because it lacks clear mathematical operators. This ambiguity leads to multiple interpretations, each yielding a different result. The most common interpretations are:
- Interpretation 1: Treating it as a string of numbers: In this case, "1 1 16" can be interpreted as "one, one, sixteen" with the division applied sequentially.
- Interpretation 2: Implicit addition: Here, it's assumed that there are implicit addition operators between the numbers, turning the expression into "(1 + 1 + 16) / 2".
- Interpretation 3: Misunderstanding of Order of Operations: This involves misapplying the division operator without considering proper mathematical rules.
Let’s explore each of these interpretations in detail and find the correct solution.
Interpretation 1: Sequential Interpretation
In this scenario, the problem is treated as a sequence of numbers undergoing division.
- Initial Sequence: 1, 1, 16
- Applying the division: The interpretation would be to divide 16 by 2.
Calculation:
- 16 / 2 = 8
This interpretation assumes that only the last number, 16, is being divided by 2, while the other numbers, 1 and 1, remain unchanged.
Result:
- 1, 1, 8
This approach, however, doesn't align with standard mathematical practices. Division is usually applied within a structured mathematical expression rather than arbitrarily applied to a number in a sequence.
Interpretation 2: Implicit Addition
The second interpretation involves assuming addition operators between the numbers, turning the expression into a standard arithmetic problem.
- Modified Expression: (1 + 1 + 16) / 2
Here, we assume that the numbers 1, 1, and 16 are intended to be added together before being divided by 2.
Calculation:
- Addition: 1 + 1 + 16 = 18
- Division: 18 / 2 = 9
In this interpretation, the expression is seen as a sum being divided by 2, which is a common and logical approach in mathematics.
Result:
- 9
Interpretation 3: Misunderstanding of Order of Operations
The third interpretation might arise from a misunderstanding of the order of operations. If someone incorrectly applies the division without considering the implicit addition, they might perform the operations in a manner that violates mathematical rules.
Incorrect Calculation:
- Incorrect Division: 16 / 2 = 8
- Adding the remaining numbers: 1 + 1 + 8 = 10 (This is one way a misunderstanding could lead to an incorrect result.)
Or, another incorrect sequence:
- First division: 1 / 2 = 0.5
- Second division attempt: 1 / 0.5 = 2 (This step doesn't follow standard order of operations.)
- Adding 16: 2 + 16 = 18 (Then dividing by an implied 2 later is still off.)
This approach is flawed because it doesn't respect the standard mathematical conventions of evaluating expressions.
Result:
- Incorrect results such as 10 or 18, depending on the specific misunderstanding.
The Correct Approach: Implicit Addition
Considering the context and mathematical conventions, the most logical and accurate interpretation of the expression "1 1 16 divided by 2" is to treat it as an implicit addition problem:
- (1 + 1 + 16) / 2
This approach aligns with how mathematical expressions are typically evaluated, especially when there are no explicit operators provided.
Calculation:
- Addition: 1 + 1 + 16 = 18
- Division: 18 / 2 = 9
Final Result:
- 9
This result is derived from the most reasonable and mathematically sound interpretation of the given expression.
Order of Operations: PEMDAS/BODMAS
To further clarify why the implicit addition approach is correct, it's important to understand the order of operations, often remembered by the acronyms PEMDAS or BODMAS:
- PEMDAS: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction.
- BODMAS: Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
In both acronyms, the order indicates the sequence in which mathematical operations should be performed. In our case, the implicit addition inside the parentheses (or brackets, depending on the notation) should be performed before the division.
Examples and Scenarios
Let's consider a few examples and scenarios to illustrate the importance of the correct interpretation and order of operations.
Example 1: Distributing Apples
Imagine you have 1 apple, then you get another apple, and then you receive 16 apples. You want to divide the total number of apples equally between two people. The correct way to calculate this is:
- Total apples: 1 + 1 + 16 = 18
- Divide by 2: 18 / 2 = 9
Each person gets 9 apples.
Example 2: Calculating Average Score
Suppose you have three scores: 1, 1, and 16. To find the average of these scores, you would add them together and then divide by the number of scores (which is 3). However, if you only want to divide the sum of the first two scores and then add the third, that's a different operation. In our case, we only divide the sum:
- Sum of scores: 1 + 1 + 16 = 18
- Divide by 2: 18 / 2 = 9
The result is 9.
Example 3: Simplifying Expressions
Consider the expression "2 + 3 + 4 divided by 2". According to the order of operations, you would first perform the addition and then the division:
- Addition: 2 + 3 + 4 = 9
- Division: 9 / 2 = 4.5
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Several common mistakes can lead to incorrect solutions when dealing with ambiguous expressions like "1 1 16 divided by 2".
- Ignoring Implicit Operators: Failing to recognize that the expression likely implies addition between the numbers.
- Misapplying Order of Operations: Performing division before addition, which violates PEMDAS/BODMAS.
- Sequential Calculation: Treating the problem as a sequence of numbers undergoing division without a clear mathematical structure.
To avoid these mistakes:
- Always look for implicit operators: When an expression lacks explicit operators, consider the possibility of addition or other operations that might be implied by the context.
- Follow the order of operations: Adhere to PEMDAS/BODMAS to ensure that operations are performed in the correct sequence.
- Clarify ambiguity: If an expression is unclear, seek clarification to ensure that you understand the intended mathematical operation.
The Importance of Clear Mathematical Notation
The ambiguity in "1 1 16 divided by 2" underscores the importance of clear mathematical notation. In mathematics, precise notation is essential to avoid confusion and ensure that expressions are interpreted correctly. Using parentheses, brackets, and explicit operators helps to eliminate ambiguity and guide the reader to the correct solution.
For instance, if the intention is to add the numbers and then divide by 2, the expression should be written as:
- (1 + 1 + 16) / 2
If the intention is to divide only the last number by 2, the expression should be written as:
- 1 + 1 + (16 / 2)
By using clear notation, we eliminate the possibility of misinterpretation and ensure that everyone arrives at the same correct answer.
Advanced Interpretations and Edge Cases
While the most reasonable interpretation of "1 1 16 divided by 2" is (1 + 1 + 16) / 2, it's worth considering advanced interpretations and edge cases, though they are less likely in a typical context.
Interpretation as Mixed Fractions
In some contexts, the expression might be interpreted as mixed fractions, although this is highly unlikely given the spacing and wording.
- Expression: 1 1/16 divided by 2
- Convert to improper fraction: 1 1/16 = (1 * 16 + 1) / 16 = 17/16
- Divide by 2: (17/16) / 2 = 17/32
Result:
- 17/32
This interpretation is less likely because it assumes a specific format of mixed fractions, which is not explicitly indicated in the original expression.
Interpretation Using Continued Fractions
Another advanced interpretation involves continued fractions, though this is also unlikely.
- Expression: 1 + 1/(16/2)
- Simplify: 16/2 = 8
- Expression: 1 + 1/8
- Result: 9/8
This interpretation is also unlikely because it involves assumptions about the structure of continued fractions that are not explicitly stated.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the expression "1 1 16 divided by 2" is ambiguous due to the lack of clear mathematical operators. The most logical and mathematically sound interpretation is to treat it as an implicit addition problem:
- (1 + 1 + 16) / 2 = 9
This interpretation aligns with standard mathematical conventions and the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS). While other interpretations are possible, they are less likely and often involve making assumptions that are not explicitly stated in the original expression.
To avoid confusion, it's essential to use clear mathematical notation and adhere to the order of operations. By doing so, we can ensure that mathematical expressions are interpreted correctly and that everyone arrives at the same accurate solution.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 1 16 Divided By 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.